Identifying and Managing Houseplant Pests Effectively


Intro
Houseplants are cherished by many for their aesthetic appeal and their role in enhancing indoor environments. However, these beautiful additions to our homes can be vulnerable to a variety of pests. Understanding common pests that affect houseplants is crucial for maintaining their health and beauty. This article dives into their identification, prevention, and control measures. By gaining insight into the life cycles of these pests, gardeners and homeowners can take proactive steps.
This guide also highlights sustainable practices for managing infestations. It aims to provide practical knowledge that empowers readers to create a thriving indoor garden.
Identifying Common Pests
It is essential to recognize common pests early to prevent significant damage. Here are some frequent offenders:
- Aphids: Small, soft-bodied insects that come in various colors. They often cluster on new growth.
- Spider Mites: Microscopic pests that cause stippling on leaves. Look for fine webbing in infested areas.
- Mealybugs: White, cottony masses found in leaf axils. They can create a sticky residue.
- Scale: Small, hard insects that resemble bumps on branches. They suck plant fluids and weaken the plant.
Life Cycles of Pests
Understanding the life cycle of pests is crucial. For example, aphids reproduce rapidly, leading to a quick population surge. Knowing when these pests thrive helps in targeting control efforts effectively.
Prevention Strategies
Preventing a pest infestation is generally easier than managing one after it occurs. Here are some effective strategies:
- Regular Inspection: Check plants weekly for any signs of pests.
- Proper Watering: Overwatering can create conditions for pests like fungus gnats.
- Air Circulation: Ensure adequate airflow as stagnant conditions attract pests.
Companions and Natural Defenses
Utilizing companion planting can deter pests. For instance, planting marigolds alongside your houseplants can be beneficial.
Control Measures
If prevention fails, control measures need to be employed. The following methods have proven effective:
- Insecticidal Soap: This is a safe option for many household pests. Apply to affected areas as per product instructions.
- Neem Oil: A natural pesticide that disrupts pest growth. It is effective against various insects, including spider mites and aphids.
- Manual Removal: For smaller infestations, simply wiping or removing pests can be effective.
"An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure."
Sustainable Practices
Adopting sustainable practices is crucial for plant health. Some examples include:
- Biological Control: Introducing beneficial insects like ladybugs can keep pest populations in check.
- Homemade Solutions: Use natural remedies like diluted vinegar or dish soap.
Closure
Preamble to Houseplant Pests
Houseplants bring life to our interiors, enhancing aesthetics and improving air quality. However, they can become targets for various pests. Understanding these common pests is vital for maintaining plant health and ensuring a thriving indoor environment. Effective management can prevent infestations that can compromise the beauty and vitality of plants.
Pests can rapidly multiply, and their presence often goes unnoticed by untrained eyes. Consequently, infestation may lead to significant damage, potentially resulting in the death of plants. This article shines a light on how to identify and manage these nuisances. By delving deep into the world of houseplant pests, you’ll become equipped with the knowledge necessary to preserve the integrity of your indoor garden.
The Importance of Pest Management
Pest management is an essential aspect of successful houseplant care. It goes beyond mere aesthetics; it affects the overall health and longevity of your plants. Effective pest control safeguards your plants from diseases that pests can introduce. Furthermore, proactive measures can save time and resources by preventing larger infestations that may require more drastic control methods later.
In addition, the significance of pest management extends to one's mental well-being. Houseplant enthusiasts often derive joy from nurturing their plants. When pests invade, this joy can quickly diminish. Therefore, understanding pest management is not only about plants but also about nurturing the emotional benefits derived from gardening.
Types of Houseplants Affected
Several types of houseplants are susceptible to pest infestations. Some common varieties include:
- Foliage Plants: Popular examples like the Monstera and Pothos can attract aphids and spider mites. Their leaves provide a perfect place for pests to feed.
- Flowering Plants: Plants such as African Violets can suffer from whiteflies and mealybugs, which appreciate the sugary sap in their flowers.
- Succulents and Cacti: While resilient, species like Echeveria may experience fungus gnat problems if overwatered.

Understanding the vulnerability of your specific houseplants is crucial in adopting a targeted approach for prevention and management. By identifying which plants are affected and their specific needs, you can create a more conducive environment for healthy growth.
"A well-maintained houseplant can be both a beautiful addition to any home and a source of personal pride. However, knowledge of common pests is needed to sustain that beauty."
This blend of awareness of pest liabilities and effective management strategies ensures that your indoor garden thrives.
Identifying Common Pests
Identifying common pests is a fundamental aspect of maintaining the health and vitality of houseplants. Recognizing the signs of pest presence early can prevent extensive damage and save plants from potential demise. Many pests are small and often go unnoticed until they have established a significant population. This can create a cycle of damage that becomes hard to manage.
By being familiar with the appearance and behavior of prevalent pests, plant owners can take timely action. This preemptive approach can save time, resources, and unnecessary stress associated with an infested plant. Moreover, early identification allows for the consideration of eco-friendly pest management solutions, which align with the growing preferences for sustainable gardening practices.
Aphids
Aphids are small, soft-bodied insects that can be found in a variety of colors, including green, black, and yellow. They tend to cluster on the undersides of leaves and around new growth. These pests feed on plant sap, weakening the plant and potentially stunting its growth. Aphids can also lead to the development of sooty mold, which forms from the honeydew they excrete. This mold can inhibit photosynthesis and lead to further issues.
To manage aphids, inspect your plants regularly, especially during the growing season. Multiple methods can be employed, such as introducing natural predators like ladybugs or using insecticidal soap for more robust infestations.
Spider Mites
Spider mites are minuscule pests that are often difficult to see without a magnifying glass. These pests thrive in hot, dry conditions and can cause yellowing leaves and webbing on the plant, particularly between leaves. Their feeding results in stippling on the leaves and can lead to significant foliage loss if not addressed promptly.
Regular misting or introducing humidity to the environment can deter spider mites. If an infestation occurs, a thorough washing of the plant with water or using commercial miticides may be necessary.
Mealybugs
Mealybugs are soft-bodied insects covered in a white, waxy coating, making them easy to recognize. They often congregate in leaf axils and at the base of stems. Feeding on plant sap, they weaken the plant and produce honeydew, leading to sooty mold growth. Mealybugs can also cause leaf drop and diminished overall health of the plant.
To control mealybugs, use a cotton swab dipped in alcohol to remove them manually. If the problem persists, consider insecticidal soap or neem oil treatments which are effective against this pest.
Whiteflies
Whiteflies are tiny, moth-like insects that can be found underneath leaves. Similar to aphids, they suck sap from plants and can produce honeydew. High populations can lead to yellowing leaves and reduced vigor in plants. They thrive in warm conditions, making them common in indoor gardens.
Management of whiteflies typically involves the use of sticky traps and maintaining good airflow around plants. Additionally, biological controls like parasitic wasps can provide an effective solution in severe cases.
Fungus Gnats
Fungus gnats are small flying insects commonly found in potting soil. The larvae feed on organic matter and plant roots, causing weak growth and potential decline of your houseplants. While adult fungus gnats are merely a nuisance, their larvae can be quite damaging.
To control fungus gnats, allow the soil to dry out between watering and consider using a well-draining potting mix. Sticky traps can be placed near the soil surface to capture adult gnats and reduce their population.
Life Cycle of Common Houseplant Pests
Understanding the life cycle of common houseplant pests is fundamentally important in addressing infestations effectively. This section sheds light on how pests reproduce and the duration of their life cycles, which can directly impact their management and control strategies. By comprehending these elements, homeowners and gardening aficionados can take informed actions to mitigate pest issues before they escalate into serious problems.
Understanding Pest Reproduction
The reproduction of houseplant pests varies among species, but the general process follows a distinct pattern. Many common pests, such as aphids and spider mites, reproduce rapidly. For instance, aphids can give birth to live young multiple times per week, leading to exponential population growth if not managed.
In some cases, pests might engage in sexual reproduction, while others practice parthenogenesis, which allows them to produce offspring without mating. This can even occur in conditions that may not be conducive for traditional mating. Understanding whether a pest reproduces sexually or asexually helps gardeners predict population increases.
Monitoring pest populations is crucial. When the number of insects rises suddenly, it’s often due to their rapid reproduction rate. Regular inspections can catch these populations early, allowing for timely action.
Duration of Life Cycles
The life cycle duration of houseplant pests can vary significantly, typically spanning anywhere from a few days to a few months based on environmental conditions, species, and available food sources. For instance:
- Aphids: Their life cycle can be completed in as little as one week under optimal conditions. This short duration allows for swift outbreaks.
- Spider Mites: These can take about one to three weeks to complete their life cycle, again depending on temperature and humidity.
- Mealybugs: They have a longer life cycle, often requiring several months to mature and reproduce.
Factors such as light, temperature, and humidity play a crucial role in these durations. When conditions are favorable, pests develop quicker; when unfavorable, their growth may stagnate.
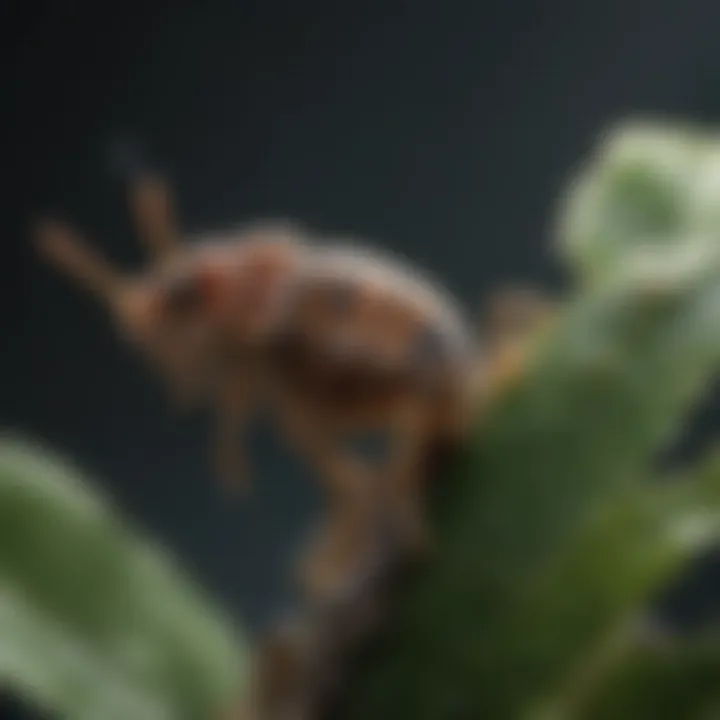


Key Insight: The sooner you can respond to an infestation, the easier it will be to manage. Knowing the life cycle of pests aids in planning eradication strategies that match their reproductive phases, ensuring a more effective approach.
Signs of Infestation
Identifying the signs of infestation in houseplants is a critical aspect of pest management. Recognizing these signs early can prevent extensive damage to plants and ensure their overall health. The presence of pests can lead to diminished plant vitality, increasing stress levels in your greenery. Therefore, being vigilant helps in implementing effective measures before the issues escalate.
Visible Damage to Leaves
One of the most immediate indicators of pest activity is visible damage to leaves. This damage can manifest in various forms, including yellowing, wilting, or distortion of plant foliage.
Often, pests like aphids and spider mites feed on the sap of the leaves. This feeding causes leaves to lose their natural green color, turning them yellow or brown. Moreover, leaves may begin to curl or develop small holes as a result of these feeding habits. If left unchecked, this damage can worsen, leading to leaf drop or killing the entire plant. Acutely, timely observation is needed to identify such issues. Look for:
- Yellowing of leaves
- Wilting or drooping
- Holes or unusual spots on leaf surfaces
Webbing and Sticky Residues
Another telling sign is the presence of webbing and sticky residues on the leaf surface. Webbing is often associated with spider mites, which create fine webs to protect themselves while they feed. This webbing can cover entire plants, making them look unkempt and unhealthy.
Sticky residues, on the other hand, often come from honeydew secreted by many pest species like aphids and mealybugs. This substance can attract other pests, such as ants, and may lead to additional issues like sooty mold. To address webbing or sticky residues, look for:
- Fine silk-like webs, especially on the undersides of leaves
- A shiny, sticky coating on leaves and surrounding surfaces
Presence of Insects
Finally, the most straightforward way to identify an infestation is by the direct presence of insects. Sometimes, adult pests can be seen crawling on leaves, stems, or surrounding areas. Their shapes and sizes can vary widely, which can make identification challenging. For example, aphids are small and often found in clusters, while mealybugs appear as white cottony masses.
It is essential to inspect plants regularly for these insects. Use bright light to search for any movement across the leaves or stems. Key things to look out for include:
- Small insects or clusters on or near plants
- Moving pests, such as whiteflies, or minute creatures like fungus gnats
Catching pests early can significantly reduce their impact on your plants.
Preventing Pest Infestations
Preventing pest infestations is essential for maintaining healthy houseplants. An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure, especially when it comes to the delicate balance that indoor plants require. By addressing potential issues before they arise, plant owners can save time, money, and stress in the long run. Furthermore, taking proactive measures helps to cultivate a thriving environment for your plants rather than a battleground against pests.
Choosing the Right Soil
The foundation of any healthy plant is the soil in which it grows. Choosing the right soil is pivotal to preventing pest infestations. Many common pests thrive in poor-quality soil that retains excess moisture or lacks essential nutrients.
Opt for a high-quality potting mix that provides proper drainage and aeration. Consider blends that include compost or other organic materials. This approach not only enhances nutrient availability but also supports beneficial microorganisms that can deter pests. It is important to steer clear of garden soil, as it can contain pathogens and unwanted pests detrimental to houseplants.
Maintaining Proper Watering Practices
Proper watering practices are crucial for preventing pest outbreaks. Over-watering is a common mistake that creates a favorable environment for pests like fungus gnats. These insects enjoy damp environments where they can reproduce quickly.
It is essential to understand the specific water requirements for each plant species. Typically, allow the top inch of soil to dry out before watering again. Ensure that pots have adequate drainage holes to prevent standing water, which can lead to root rot and attract unwanted insects. Monitoring the humidity levels in your home can also prove beneficial. Using a humidity meter can help maintain optimal levels for health plant growth.
Regular Plant Inspections
Regular inspections of your plants should become a routine part of houseplant care. Observing your plants closely allows for the early detection of any signs of pest infestations. Look for discolored leaves, webbing, or sticky residues that may indicate a problem.
Inspect both the top and underside of leaves, as well as the stems. Turning pots to view all angles helps in spotting potential concerns. Create a schedule for these inspections—perhaps weekly or bi-weekly—to develop a keen eye for your plants’ health. Record any changes in growth or appearance. Early intervention can often stop pest problems before they escalate into infestations.
Control Measures for Pests
In managing houseplant pests, effective control measures are essential. They help alleviate damage and ensure the long-term health of indoor plants. Taking a proactive approach means addressing infestations before they escalate. Therefore, understanding the nuances of these measures is vital for every houseplant enthusiast.
Chemical Treatments
Chemical treatments have their place in pest control. They usually target a range of common pests. Products containing insecticidal soap or neem oil are popular choices. These treatments disrupt the life cycle of insects, thereby reducing their populations. However, using chemicals requires careful consideration. Not all chemicals are safe for every plant. It is crucial to read labels and follow application instructions to avoid harming your plants. The timing of application matters as well. Typically, early morning or late evening is best, avoiding direct sunlight.
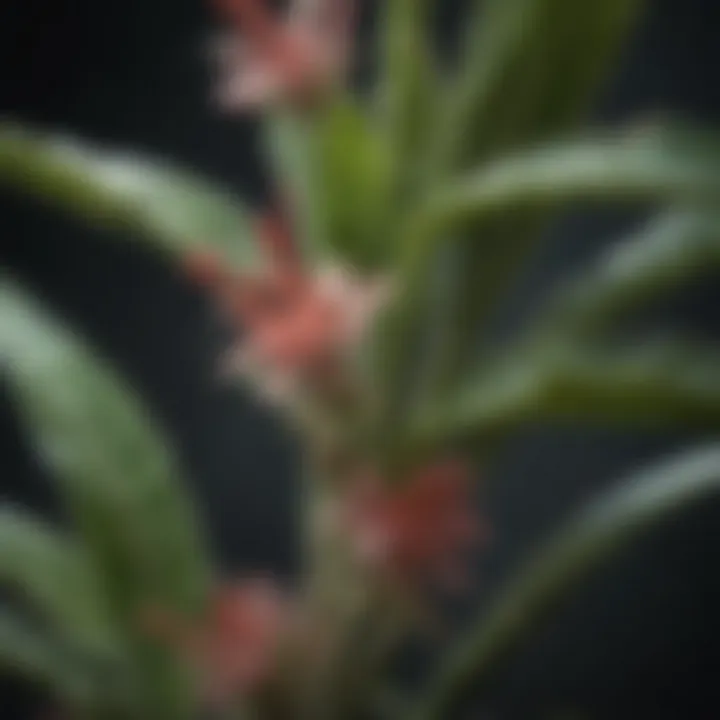


Organic Solutions
For those interested in eco-friendly alternatives, organic solutions are a sound choice. These options are often less toxic and safer for plants and humans. Common organic treatments include diatomaceous earth and essential oils. For example, a mixture of water and a few drops of peppermint oil can repel various pests. Another strategy is introducing beneficial insects such as ladybugs or lacewings, which are natural predators of harmful insects.
Organic solutions may take longer to see results, but they promote healthier ecosystems. They align well with the broader trend of sustainable gardening practices.
Physical Removal Techniques
Physical removal techniques stand as a direct way to manage pests. Hands-on methods can be particularly effective for localized infestations. Gardeners can simply remove pests by hand or wash them off with a strong stream of water. This approach reduces populations without chemicals. Another effective method is pruning affected leaves. Doing so not only removes pests but also helps in preventing spread to other areas.
Sustainable Practices for Pest Management
Sustainable practices for pest management are crucial for maintaining the health of houseplants. In recent years, concerns around chemical pest control have increased. Sustainable methods promote ecological balance and reduce harm to both plants and the environment. By focusing on natural solutions, homeowners can manage infestations effectively while also being mindful of their impact on biodiversity.
Implementing sustainable practices can lead to healthier indoor environments and plants that thrive. These methods encourage a more holistic approach, recognizing the interconnectedness of all life forms in an ecosystem. Such an approach involves considering both pest control and plant care strategies that minimize chemical use, promote beneficial organisms, and encourage a balanced habitat.
Integrating Beneficial Insects
Integrating beneficial insects is an effective strategy in sustainable pest management. These insects, such as ladybugs, lacewings, and parasitic wasps, can help control pest populations naturally. For example, ladybugs feed on aphids, while lacewings are known for their ability to consume various pest species.
Homeowners can attract beneficial insects by planting native flowers and herbs. Some good options include marigolds, dill, and yarrow. Avoiding broad-spectrum insecticides is also essential, as they can kill beneficial insects along with pests. Instead, consider employing targeted treatments that preserve the health of these natural allies.
Using Companion Planting Techniques
Companion planting techniques involve placing certain plants together to create a mutually beneficial environment. Specific plants can repel pests, attract beneficial insects, or enhance the growth of nearby plants. For instance, the marigold plant is known to repel nematodes and aphids, making it a good companion for vulnerable houseplants.
Understanding plant relationships can enhance your indoor garden's resilience. Research the needs and characteristics of both plants involved. This practice not only deters pests but also fosters a dynamic ecosystem in your home.
Encouraging Biodiversity in Indoor Spaces
Encouraging biodiversity in indoor spaces can significantly contribute to pest management efforts. A diverse array of plant species creates a more resilient environment. By selecting a variety of plants with different signatures, indoor spaces can attract diverse insects that dissuade harmful pests.
To promote biodiversity:
- Include a mix of flowering, foliage, and herbaceous plants.
- Maintain varied light and water needs to support multiple species.
- Consider incorporating plants that attract pollinators, which can also support beneficial insect populations.
A biodiverse indoor garden acts as a buffer against pests, reducing the likelihood of widespread infestations. Together, these practices can foster a thriving ecosystem that benefits both plants and the environment.
Impact of Pests on Houseplant Health
Understanding the impact of pests on the health of houseplants is critical for anyone involved in indoor gardening. Pests are not just nuisances; they can severely affect a plant's vitality. The presence of pests often leads to stress in plants, which can compromise their growth and aesthetics. Analyzing how pests affect plant integrity is essential for effective management and prevention strategies.
Stress on Plants
Pests subject houseplants to various types of stress. When pests infest a plant, they extract vital nutrients, which leads to weakened plants. This nutrient deficiency causes the plants' metabolic processes to slow down. As a result, you may notice symptoms like wilting leaves or premature leaf drop. Stress also reduces a plant's resilience against diseases and environmental factors. An infested plant is less capable of coping with changes in humidity or light levels, making it vulnerable to further complications in its care.
Stress management is crucial for maintaining a healthy indoor garden. Regular inspections can help identify early signs of pest infestations.
Reduced Growth and Foliage Quality
Infestations can severely impact a plant's growth rate. When pests like aphids or spider mites invade, plants experience stunted growth. The energy that should go into developing new leaves, flowers, or roots is diverted to fighting off these pests. Under severe infestations, the foliage may develop unsightly spots or yellowing, which diminishes both the aesthetics and health of the plant.
The quality of foliage is vital to overall plant health. Healthy, lush leaves not only support photosynthesis but also contribute to the plant’s ability to survive and thrive indoors. Poor-quality foliage can hinder the plant's ability to photosynthesize effectively, which adds to its stress and reduces its overall health.
Addressing pest issues promptly can protect the vitality of houseplants and maintain their beauty.
Epilogue
Summary of Key Points
- Identification is the first step in managing pests. Being able to recognize pests like aphids, spider mites, and mealybugs will allow for timely intervention.
- Prevention is more effective than treatment. Practices such as choosing the right soil, maintaining proper watering, and conducting regular inspections can mitigate potential infestations.
- Different control measures exist, including chemical treatments, organic solutions, and physical removal techniques. Each has its place depending on the severity of the infestation and environmental considerations.
- Understanding the impact of pests can guide decisions on care routines. Stress on plants and reduced growth signify the urgent need for pest management.
- Sustainable practices, like integrating beneficial insects and using companion planting, provide eco-friendly solutions to pest issues without compromising plant integrity.
Future Considerations for Houseplant Care
As future enthusiasts of houseplant care reflect on pest management, it will be important to stay informed about emerging pest control techniques that prioritize plant health. Research on pest-resistant plant varieties may shape future care strategies, creating an indoor gardening environment that is both beautiful and resilient. Additionally, increasing awareness of ecological impacts associated with chemical treatments will encourage the adoption of more sustainable practices.
Ultimately, the intersection of knowledge and practice will set a solid foundation for a thriving indoor gardening experience.







